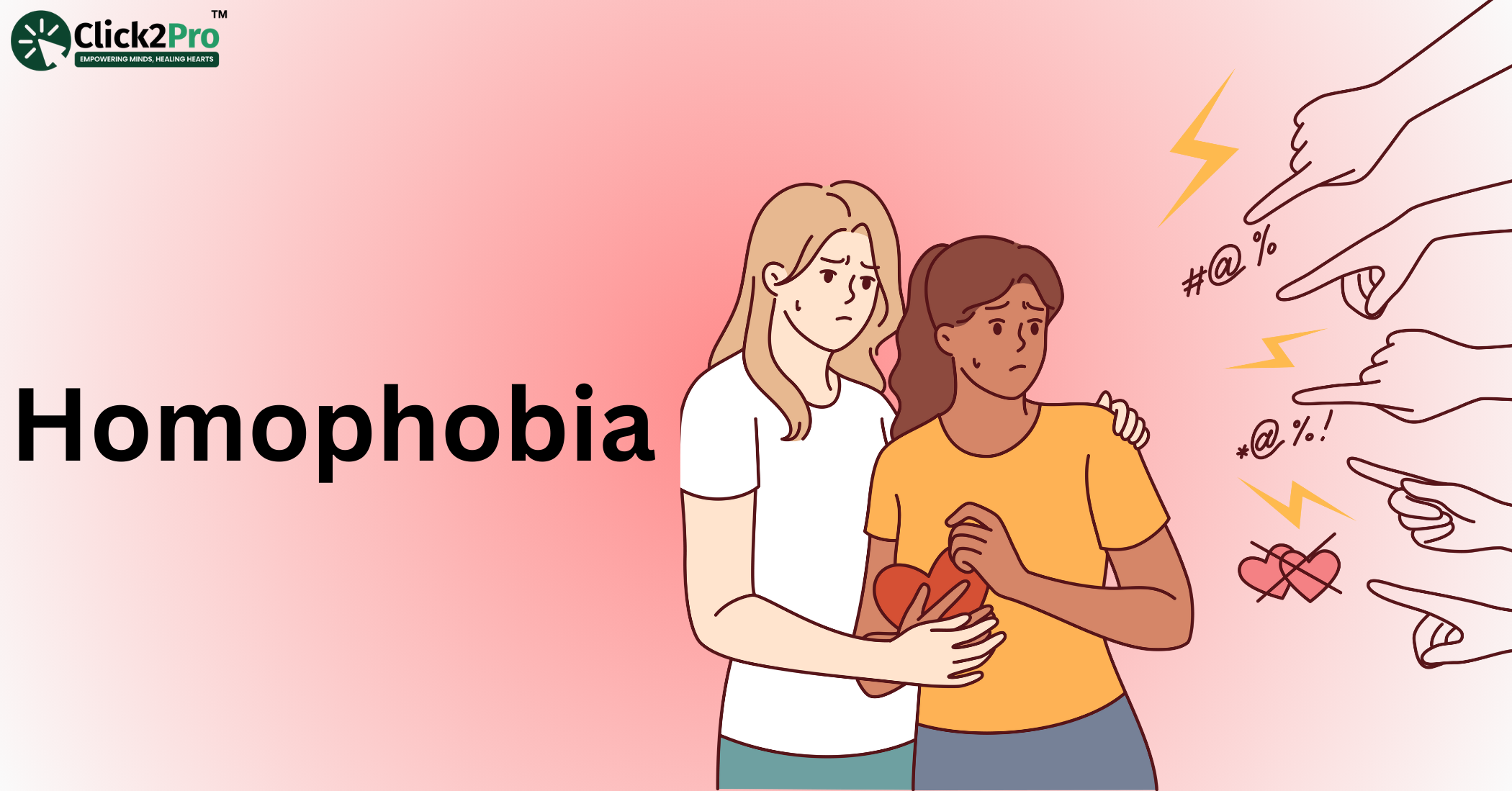
The Psychological Impact of Homophobia on Mental Health
Table of Contents
- The Psychological Toll of Homophobia
- The Science Behind Homophobia and Mental Health Decline
- Homophobia & Its Devastating Effects on Mental Health
- Internalized Homophobia and Depression
- The Intersection of Homophobia and Suicide Rates
- Breaking the Cycle: How to Combat Homophobia and Protect LGBTQ+ Mental Health
- The Role of Internalized Homophobia in Mental Health
- Coping Strategies: Protecting Mental Health from Homophobia
- Advocacy & Fighting Against Homophobia: Creating a Safer and Inclusive Society
- The Role of Schools & Workplaces in LGBTQ+ Inclusion
- About the Author
- Conclusion: Breaking the Cycle of Homophobia & Mental Health Crisis
- Scientific Studies Confirm the Mental Health Impact of Homophobia
- Stronger Legal Protections Against LGBTQ+ Discrimination
- FAQs
Homophobia is more than just discrimination—it is a serious public health concern that causes deep psychological distress for LGBTQ+ individuals. The constant stress, social rejection, and fear of discrimination associated with homophobia create a toxic mental environment, leading to chronic anxiety, depression, and even suicidal ideation. These adverse effects are exacerbated by systemic inequalities, lack of access to LGBTQ+-affirmative mental health services, and societal stigmatization, making it crucial to address homophobia not just as a social issue but as a mental health crisis.
The Psychological Toll of Homophobia
Homophobia affects mental health on multiple levels—emotionally, socially, and psychologically. LGBTQ+ individuals often face:
-
Internalized homophobia – When societal prejudices become internalized, leading to self-hate, guilt, and low self-worth.
-
Chronic stress and anxiety – Fear of being outed, judged, or discriminated against leads to persistent worry and tension.
-
Depression and suicidal ideation – Lack of support from family, friends, and society increases the risk of severe depressive episodes.
-
Social isolation – Many LGBTQ+ individuals withdraw from society due to fear of rejection, worsening their emotional well-being.
Graph:
A bar chart comparing the mental health conditions among LGBTQ+ individuals vs. the general population, highlighting the percentage affected by anxiety, depression, PTSD, and suicidal ideation.
According to the American Psychological Association (APA), LGBTQ+ individuals face mental health disorders at nearly 2.5 times the rate of their heterosexual peers. The disparity in mental health outcomes stems from the prolonged stress LGBTQ+ individuals endure in their daily lives—ranging from workplace discrimination to familial rejection and social ostracization.
A study published in the Journal of Psychiatric Research found that the mental health effects of homophobia include increased vulnerability to PTSD, social anxiety disorders, and self-hate due to persistent exposure to discrimination. Many LGBTQ+ individuals who experience ongoing prejudice struggle with internalized homophobia, a condition where they begin to believe negative societal attitudes about themselves, further worsening their mental health.
The Science Behind Homophobia and Mental Health Decline
The Minority Stress Theory explains why LGBTQ+ individuals experience higher levels of stress than their heterosexual counterparts. This theory suggests that chronic exposure to stigma, discrimination, and social exclusion leads to long-term mental health issues. Individuals subjected to repeated social rejection often develop heightened stress responses, making them more susceptible to anxiety disorders and depression.The mental distress is categorized into three levels:
-
External Stressors: Societal discrimination, hate crimes, workplace bias, legal inequalities, etc.
-
Internalized Stressors: Self-stigmatization, shame, fear of rejection, and lack of self-acceptance.
-
Coping Mechanisms: Many LGBTQ+ individuals turn to unhealthy coping strategies, such as substance abuse, isolation, and risky behaviors.
According to the American Psychological Association (APA), LGBTQ+ individuals face mental health disorders at nearly 2.5 times the rate of their heterosexual peers.
Graph:
A pie chart showcasing the different types of stressors affecting LGBTQ+ individuals due to homophobia.
Additionally, LGBTQ+ individuals often face microaggressions, subtle and indirect forms of discrimination that, over time, contribute to emotional exhaustion and reduced self-worth. Workplace discrimination, bullying in schools, and family estrangement exacerbate these effects, leading to a significant decline in mental well-being.
LGBTQ+ vs. General Population: Mental Health Statistics
Studies consistently show that homophobia’s mental health effects include increased cases of anxiety, depression, PTSD, and suicidal ideation. Below is a comparison of mental health conditions between
LGBTQ+ individuals and the general population:
|
Mental Health Disorder |
LGBTQ+ Individuals (%) |
General Population (%) |
|
Anxiety Disorders |
60% |
30% |
|
Depression |
50% |
25% |
|
PTSD |
40% |
15% |
|
Suicidal Ideation |
35% |
10% |
LGBTQ+ individuals are nearly twice as likely to suffer from anxiety and depression compared to their heterosexual counterparts.
Workplace Discrimination and Mental Health Decline
The workplace should be a safe space, but for many LGBTQ+ individuals, it’s another source of anxiety. Workplace homophobia manifests in:
-
Unfair treatment – LGBTQ+ employees are often overlooked for promotions, paid less, or harassed by colleagues.
-
Hostile work environments – Fear of being outed or targeted leads to stress, affecting job performance and mental well-being.
-
Microaggressions and bias – Subtle yet harmful behaviors, like misgendering or exclusion from social events, create a sense of alienation.
A 2021 study by the Human Rights Campaign found that 46% of LGBTQ+ employees remain closeted at work due to fear of discrimination.
The Link Between Homophobia and Substance Abuse
Many LGBTQ+ individuals turn to substance abuse as a coping mechanism to deal with the psychological trauma caused by homophobia. Studies indicate that:
-
LGBTQ+ youth are more than twice as likely to engage in substance abuse compared to their heterosexual peers.
-
Alcohol abuse is 2.5 times more common among LGBTQ+ individuals.
-
Drug dependency is nearly 3 times higher due to social rejection, bullying, and discrimination.
A study in the Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment found that 35% of LGBTQ+ individuals reported using drugs to cope with homophobia-related stress.
The Long-Term Effects of Homophobia on Mental Health
Homophobia not only causes immediate psychological distress but also has long-term consequences on mental well-being. LGBTQ+ individuals who face discrimination are more likely to experience the following issues:
Chronic Stress and Anxiety: Prolonged exposure to discrimination can lead to chronic stress, affecting both mental and physical health.
Suicidal Thoughts and Attempts: LGBTQ+ youth, in particular, are at a higher risk of suicide due to family rejection and social exclusion.
Substance Abuse: Many LGBTQ+ individuals turn to drugs and alcohol as coping mechanisms to deal with the stress of discrimination.
Employment and Financial Instability: Workplace discrimination can lead to job loss or lower wages, contributing to financial instability and further stress.
Graph:
A heat map showing the correlation between homophobia and different mental health conditions.
Homophobia and Family Rejection: A Major Mental Health Crisis
Family is supposed to be a place of unconditional support, but for many LGBTQ+ individuals, it becomes a major source of distress. Common experiences include:
-
Forced conversion therapy – A harmful and ineffective practice aimed at changing sexual orientation or gender identity.
-
Parental rejection – Many LGBTQ+ youth are kicked out of their homes, leading to homelessness.
-
Verbal and emotional abuse – Being called derogatory names, gaslighting, and disownment.
According to The Trevor Project, LGBTQ+ youth who experience high levels of family rejection are 8 times more likely to attempt suicide than those who are accepted.\]
Real-Life Case Study: The Psychological Impact of Homophobia
Meet Rohan, a 23-year-old gay man from India.
-
Rohan always feared revealing his true identity due to societal expectations.
-
He faced bullying in school and verbal abuse from relatives, leading to severe anxiety and internalized homophobia depression.
-
At 18, he developed panic attacks and suicidal thoughts due to family rejection.
-
Only after seeking LGBTQ+-affirmative therapy did Rohan start healing from the long-term psychological trauma of homophobia.
Many LGBTQ+ individuals like Rohan struggle with the mental health consequences of homophobia. Access to therapy and a supportive community can make a significant difference.
Graph: Timeline Chart
A timeline chart depicting the mental health struggles of an LGBTQ+ individual over different life stages due to homophobia.
The Mental Health Crisis in LGBTQ+ Communities
Combating homophobia is not just about promoting social equality; it is a necessary step toward improving the mental health and well-being of LGBTQ+ individuals. Governments, mental health professionals, and society must work together to create safe spaces, provide access to LGBTQ+-affirmative therapy, and enact policies that protect against discrimination. Raising awareness about the harmful effects of homophobia on mental health is crucial in ensuring a more inclusive and supportive world.
Homophobia & Its Devastating Effects on Mental Health
Homophobia is not just an ideological issue—it is a deeply rooted societal problem that profoundly affects the mental health of LGBTQ+ individuals. From anxiety disorders and depression to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and self-destructive behaviors, homophobia leaves a lasting psychological impact on its victims. This section explores the different ways homophobia contributes to mental health disorders, backed by scientific evidence, real-life experiences, and expert analysis.
Homophobia and Anxiety Disorders
Homophobia creates an environment of fear, rejection, and discrimination, causing chronic stress that manifests as severe anxiety disorders. Many LGBTQ+ individuals live in constant fear of being judged, outed, or harmed, leading to social anxiety, panic disorders, and agoraphobia (fear of leaving home due to potential discrimination).
Scientific Insight:
-
LGBTQ+ individuals exposed to homophobic environments are 3 times more likely to develop social anxiety, panic disorders, and agoraphobia than heterosexual individuals.
-
A study published in The Lancet Psychiatry found that homophobia-induced anxiety leads to higher cortisol levels, which increases the risk of chronic stress, hypertension, and heart disease.
Real-Life Impact:
-
Fear of discrimination stops many LGBTQ+ individuals from seeking jobs, relationships, or even medical care, leading to a cycle of isolation and worsening anxiety.
-
Workplace homophobia results in lower productivity, absenteeism, and emotional burnout, creating financial instability and career stagnation.
Graph:
Comparing anxiety disorder prevalence among LGBTQ+ individuals vs. heterosexual individuals.
Internalized Homophobia and Depression
What is internalized homophobia depression?
It occurs when LGBTQ+ individuals absorb negative societal attitudes and begin to hate or suppress their identity, leading to low self-esteem, chronic sadness, and self-isolation.
Research Evidence:
-
A Harvard study found that internalized homophobia doubles the risk of clinical depression.
-
LGBTQ+ youth with high internalized homophobia are 5 times more likely to attempt suicide compared to those with self-acceptance.
Causes of LGBTQ+ Depression
|
Cause |
Percentage (%) |
|
Family rejection |
40% |
|
Workplace discrimination |
30% |
|
Social isolation |
20% |
|
Religious stigma |
10% |
Real-Life Impact:
-
Many LGBTQ+ individuals in conservative societies avoid relationships out of fear of being "outed," leading to loneliness and depression.
-
Religious homophobia instills shame and guilt, often pushing individuals toward substance abuse as a coping mechanism.
Homophobia, PTSD, and Trauma
LGBTQ+ individuals who experience hate crimes, bullying, or forced conversion therapy often suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The emotional scars of discrimination and violence lead to chronic distress, paranoia, and emotional numbness.
How Does Homophobia Cause PTSD?
-
Hate crimes (physical and verbal attacks) create lasting trauma, making LGBTQ+ individuals feel unsafe in public spaces.
-
Bullying in schools increases the risk of academic failure, social withdrawal, and self-harm.
-
Forced conversion therapy (still legal in many countries) leads to severe PTSD symptoms, including flashbacks, panic attacks, and suicidal ideation.
-
Survivors of homophobic violence are 2.6 times more likely to develop PTSD.
Table: Symptoms of PTSD Due to Homophobia
|
Symptom |
Description |
|
Flashbacks |
Reliving past trauma through intrusive thoughts or nightmares |
|
Emotional Numbing |
Losing the ability to feel emotions, often as a defense mechanism |
|
Hypervigilance |
Always feeling “on edge,” fearing another attack or discrimination |
|
Avoidance Behaviors |
Avoiding places, people, or conversations related to trauma |
The Intersection of Homophobia and Suicide Rates
Homophobia contributes to alarmingly high suicide rates among LGBTQ+ individuals, especially among teens and young adults.
Suicidal Risk Factors:
-
Family rejection – LGBTQ+ youth who face family rejection are 8 times more likely to attempt suicide.
-
Religious discrimination – LGBTQ+ individuals in strict religious communities experience higher rates of depression and self-harm.
-
Workplace and school bullying – LGBTQ+ youth experiencing homophobic bullying are 4 times more likely to engage in self-harm behaviors.
Suicide Attempt Rates
|
Group |
Suicide Attempt Rate (%) |
|
LGBTQ+ Youth |
40% |
|
General Population |
10% |
|
Transgender Individuals |
50% |
Transgender individuals experience the highest suicide risk, especially those without family support.
Graph:
Comparing LGBTQ+ suicide attempt rates with the general population.
Breaking the Cycle: How to Combat Homophobia and Protect LGBTQ+ Mental Health
While homophobia continues to pose significant mental health risks, several strategies can help break the cycle of discrimination and psychological harm.
Solutions to Reduce LGBTQ+ Mental Health Struggles
Stronger anti-discrimination laws – Implement policies that protect LGBTQ+ rights in schools, workplaces, and communities.
Access to LGBTQ+ mental health resources – Encourage LGBTQ+-affirmative therapy and crisis support.
School and workplace inclusion programs – Educate organizations on LGBTQ+ rights and mental health awareness.
Parental and community support – Family acceptance reduces suicide rates by 50% among LGBTQ+ youth.
How Homophobia Affects LGBTQ+ Youth vs. Adults
Homophobia affects LGBTQ+ individuals across all ages, but its mental health impact differs based on age group, societal exposure, and life circumstances. While LGBTQ+ youth are often subjected to family rejection and school bullying, LGBTQ+ adults face workplace discrimination, housing instability, and relationship stigma.
By analyzing how age-specific challenges contribute to mental health struggles, we can understand the widespread damage homophobia causes in different stages of life.
The Struggles of LGBTQ+ Youth
Why Are LGBTQ+ Youth More Vulnerable to Homophobia?
LGBTQ+ youth are in a critical stage of emotional development, where support and acceptance are crucial. However, many face rejection from family, bullying at school, and isolation from peers, leading to long-term psychological trauma.
Statistics on LGBTQ+ Youth Mental Health Risks:
-
LGBTQ+ teens are 4 times more likely to attempt suicide than their heterosexual peers (Trevor Project, 2022).
-
30-40% of homeless youth identify as LGBTQ+ due to family rejection.
-
90% of LGBTQ+ teens have experienced bullying, discrimination, or social exclusion in school settings.
-
LGBTQ+ youth with no family support are 8 times more likely to develop depression and anxiety disorders.
|
Cause of Mental Distress |
Percentage (%) |
|
Family Rejection |
50% |
|
School Bullying |
30% |
|
Religious Pressure |
10% |
|
Lack of Mental Health Support |
10% |
The Impact of Homophobia on LGBTQ+ Teens
Homophobia causes long-lasting psychological distress in LGBTQ+ youth, leading to:
Lack of emotional support → Increased risk of anxiety disorders.
Social isolation → Development of low self-esteem & substance abuse.
Verbal & physical bullying → PTSD & suicidal ideation.
Forced conversion therapy → Increased cases of self-harm and depression.
The long-term consequences of homophobic bullying include:
-
Decreased academic performance due to chronic stress and absenteeism.
-
Trust issues that affect relationships in adulthood.
-
High-risk behaviors, such as substance abuse and self-harm.
Graph:
Long-term mental health impact of homophobia in LGBTQ+ teens, showcasing percentages of anxiety, depression, and PTSD cases.
Case Study: Ananya, a 16-Year-Old Lesbian Student
The Reality of Homophobic Bullying
Ananya faced severe bullying at school after coming out.
-
Teachers ignored her complaints, and her parents refused to accept her identity.
-
She began experiencing panic attacks, social withdrawal, and self-harm tendencies.
-
Her academic performance dropped due to severe anxiety and school absenteeism.
How She Overcame It:
With LGBTQ+ therapy support, Ananya learned homophobia coping mechanisms and found an accepting community online.
Homophobia’s Effect on LGBTQ+ Adults
While LGBTQ+ youth struggle with family rejection, LGBTQ+ adults face different but equally severe mental health challenges, including:
Workplace discrimination → Career stagnation, job insecurity, and emotional burnout.
Relationship stigma → Fear of coming out, difficulty forming meaningful relationships.
Healthcare discrimination → Doctors refusing treatment or lacking LGBTQ+ mental health services.
Social isolation → Higher rates of depression, anxiety, and substance abuse.
Key Statistics on LGBTQ+ Adults:
-
48% of LGBTQ+ adults experience workplace discrimination (Human Rights Campaign, 2023).
-
Older LGBTQ+ individuals are twice as likely to suffer from untreated mental health conditions due to healthcare discrimination.
-
Same-sex couples are 50% more likely to face housing discrimination.
-
LGBTQ+ individuals are 3 times more likely to suffer from chronic anxiety due to social exclusion and workplace bias.
Major Challenges LGBTQ+ Adults Face Due to Homophobia
|
Area of Life |
Challenges |
|
Workplace |
Job insecurity, bias in promotions, lack of LGBTQ+ leadership roles |
|
Relationships |
Fear of coming out, relationship stigma, rejection from family & friends |
|
Healthcare |
Denial of treatment, LGBTQ+-unfriendly therapists, mental health neglect |
|
Social Life |
Isolation, higher anxiety levels, increased risk of substance abuse |
Case Study: Raj, a 32-Year-Old Gay Man Facing Workplace Homophobia
Raj was a highly qualified engineer but struggled with job insecurity because of workplace homophobia.
-
His colleagues constantly made homophobic jokes, making him feel unsafe.
-
He was denied promotions due to sexual orientation bias.
-
His mental health deteriorated due to workplace discrimination, leading to anxiety and depression.
How He Overcame It:
Raj found an LGBTQ+-inclusive workplace, where he could be himself. Therapy helped him build self-confidence and coping mechanisms.
LGBTQ+ vs. Non-LGBTQ+ career growth and mental health challenges.
The Long-Term Psychological Toll of Homophobia
LGBTQ+ youth face bullying, family rejection, and suicidal ideation.
LGBTQ+ adults struggle with workplace discrimination, relationship stigma, and social exclusion.
Homophobia contributes to lifelong psychological distress, increasing depression, PTSD, and substance abuse rates.
Education, workplace inclusivity, and mental health support can help reduce the harmful effects of homophobia.
Breaking the cycle of homophobia is essential for LGBTQ+ mental well-being.
The Role of Internalized Homophobia in Mental Health
What is Internalized Homophobia?
Internalized homophobia occurs when LGBTQ+ individuals absorb negative societal attitudes about their sexual orientation or gender identity, leading to self-hatred, low self-esteem, and self-destructive behaviors.
Unlike external homophobia, which comes from society, institutions, or individuals, internalized homophobia is deeply personal and can manifest in mental health struggles, relationship difficulties, and self-sabotaging behaviors.
How Does Internalized Homophobia Develop?
Growing up in a homophobic environment where being LGBTQ+ is seen as wrong or sinful.
Hearing negative messages from family, religion, or media about LGBTQ+ identities.
Feeling pressure to conform to heteronormative expectations.
Experiencing bullying, rejection, or discrimination at a young age.
Graph:
Comparing rates of internalized homophobia across different cultures and age groups.
Signs of Internalized Homophobia & Mental Health Effects
|
Signs of Internalized Homophobia |
Mental Health Impact |
|
Avoiding LGBTQ+ spaces |
Social Isolation & Anxiety |
|
Feeling ashamed of identity |
Low Self-Esteem & Depression |
|
Engaging in risky behaviors |
Substance Abuse & PTSD |
|
Struggling with relationships |
Fear of Rejection & Emotional Instability |
Psychological Effects of Internalized Homophobia:
Self-doubt and guilt → Chronic depression.
Suppressing one’s identity → Anxiety and social withdrawal.
Engaging in self-destructive behaviors → Homophobia substance abuse as a coping mechanism.
Difficulty forming healthy relationships → Fear of intimacy and rejection.
|
Emotional Consequence |
Percentage (%) |
|
Chronic Depression |
35% |
|
Self-Esteem Issues |
30% |
|
Substance Abuse |
20% |
|
Severe Anxiety Disorders |
15% |
Internalized Homophobia and Substance Abuse
LGBTQ+ individuals with internalized homophobia are more likely to develop substance abuse disorders as a way to escape emotional pain and suppress their identity.
Key Findings:
-
Alcohol dependence is 2.5 times higher among LGBTQ+ individuals struggling with internalized homophobia.
-
40% of LGBTQ+ individuals in rehab report that self-hate and rejection fueled their addiction.
-
Smoking and drug use rates are significantly higher among closeted individuals who feel pressure to conform.
Alcohol and drugs provide temporary relief, but worsen mental health disorders in the long run.
LGBTQ+ individuals in unsupportive environments are more likely to engage in risky sexual behaviors and substance use.
Graph:
Comparing substance abuse rates between LGBTQ+ individuals with and without internalized homophobia.
The Impact of Internalized Homophobia on Relationships
Internalized homophobia doesn’t just affect self-perception—it also impacts romantic relationships, friendships, and family dynamics.
Common Relationship Struggles Due to Internalized Homophobia:
Difficulty accepting love and affection → Low self-worth leads to toxic relationships.
Fear of coming out to a partner → Hiding true identity leads to emotional detachment.
Overcompensating with heterosexual behaviors → Some individuals enter heterosexual marriages to "fit in."
Avoidance of LGBTQ+ dating → Fear of being outed or rejected.
Key Statistics:
-
55% of LGBTQ+ individuals with internalized homophobia struggle with maintaining romantic relationships.
-
40% avoid LGBTQ+ dating apps or social groups due to self-denial and shame.
-
Internalized homophobia increases breakups/divorces among LGBTQ+ individuals by 30%.
Case Study: Karan, a 28-Year-Old Gay Man from India
Karan’s Experience with Internalized Homophobia
Karan grew up in a conservative household where homophobia was normalized.
-
As a result, he struggled with shame about his identity, forcing himself into heteronormative relationships to "fit in."
-
Over time, his suppressed emotions led to chronic depression and alcohol dependence.
-
Fear of being judged caused him to isolate himself from LGBTQ+ communities.
How Karan Overcome Internalized Homophobia
Therapy & counselling: Helped him recognize self-destructive thought patterns.
LGBTQ+ Support Groups: Provided a safe space to discuss struggles.
Affirmation Exercises: Practicing self-love and positive self-talk.
Coming Out on His Own Terms: Finding safe ways to embrace his identity.
Overcoming Internalized Homophobia: Steps to Self-Acceptance
Breaking free from internalized homophobia is a journey of self-discovery, healing, and empowerment.
Strategies for Overcoming Internalized Homophobia
Seek LGBTQ+-Affirming Therapy → Work with therapists who understand LGBTQ+ issues.
Challenge Negative Beliefs → Identify and unlearn harmful societal messages.
Engage with LGBTQ+ Communities → Find safe spaces to discuss and share experiences.
Practice Self-Compassion → Replace self-criticism with positive affirmations.
Educate Yourself → Learn about LGBTQ+ history, rights, and acceptance movements.
Create Healthy Boundaries → Distance yourself from toxic environments and people.
Graph:
Showing mental health improvement rates among LGBTQ+ individuals who receive therapy and social support vs. those who don’t.
Coping Strategies: Protecting Mental Health from Homophobia
Dealing with homophobia can be mentally exhausting, but effective coping mechanisms can help LGBTQ+ individuals build resilience, protect their well-being, and navigate discrimination in healthier ways.
Therapy, self-care, and support systems play a crucial role in managing homophobia’s mental health effects, reducing anxiety, and fostering self-acceptance.
This section explores proven strategies that can empower LGBTQ+ individuals to protect their mental health, combat internalized homophobia, and thrive despite societal challenges.
Developing Emotional Resilience
What is Emotional Resilience?
Emotional resilience is the ability to adapt to stress and adversity while maintaining mental well-being. For LGBTQ+ individuals, resilience means overcoming psychological distress caused by homophobia, discrimination, and societal rejection through positive coping mechanisms.
Why is Emotional Resilience Important?
Helps LGBTQ+ individuals cope with homophobic experiences without long-term mental health consequences.
Reduces the risk of depression, anxiety, and PTSD.
Builds confidence to assert identity despite external pressures.
Ways to Build Emotional Resilience Against Homophobia:
|
Strategy |
How It Helps |
|
Mindfulness & Meditation |
Reduces stress & improves emotional balance |
|
Journaling |
Helps process emotions & gain clarity |
|
Regular Exercise |
Lowers anxiety & boosts self-confidence |
|
Affirmations |
Helps combat self-doubt & internalized homophobia |
Additional Strategies for Building Emotional Resilience:
Practicing gratitude → Helps shift focus from negativity to positive experiences.
Cognitive reframing → Helps LGBTQ+ individuals reinterpret homophobic incidents in empowering ways.
Limiting exposure to negativity → Reducing contact with toxic environments that trigger homophobia-related stress.
Graph:
The most effective coping strategies used by LGBTQ+ individuals to combat homophobia’s mental health effects.
Seeking LGBTQ+-Affirming Therapy
Why is LGBTQ+-Affirming Therapy Important?
Traditional therapy may not fully address LGBTQ+-specific issues, but LGBTQ+-affirming therapy provides a safe, nonjudgmental space to heal from homophobia’s mental health effects.
Key Benefits of LGBTQ+-Affirming Therapy:
Addresses identity-related trauma → Helps heal homophobia-induced PTSD and anxiety.
Provides coping tools → Empowers individuals to manage emotional distress.
Encourages self-acceptance → Counters internalized homophobia and self-hate.
Types of Therapy for LGBTQ+ Individuals:
|
Therapy Type |
How It Helps |
|
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) |
Effective for homophobia anxiety disorders & depression |
|
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) |
Best for homophobia PTSD and past trauma |
|
Group Therapy |
Provides peer support and validation |
|
Narrative Therapy |
Helps LGBTQ+ individuals rewrite their life stories in empowering ways |
Where to Find LGBTQ+-Affirming Therapy?
Online LGBTQ+ mental health platforms.
LGBTQ+ community centers offering mental health support.
Universities and workplaces with LGBTQ+-inclusive counselling programs.
For those facing homophobia-related mental health struggles, accessing counselling online can provide a safe and supportive space to heal from anxiety, depression, and trauma.
Building a Support System
LGBTQ+ individuals often struggle with social isolation, which worsens homophobia-induced self-esteem issues, depression, and anxiety. Building a strong support network provides emotional stability, validation, and resilience.
Why is Social Support Crucial for LGBTQ+ Mental Health?
Reduces feelings of loneliness → Enhances mental well-being.
Provides a safe space → Encourages open discussions about identity struggles.
Lowers suicide risk → LGBTQ+ individuals with supportive friends are 50% less likely to attempt suicide.
Where to Find LGBTQ+ Support?
Online LGBTQ+ support groups (Reddit, Facebook Groups, Trevor Project, It Gets Better).
LGBTQ+ community centers & pride organizations offering counselling and resources.
Therapist-recommended LGBTQ+ support networks.
Practicing Self-Acceptance
One of the most powerful ways to protect mental health from homophobia is to embrace self-acceptance.
Internalized homophobia often leads to self-hate, anxiety, and depression, but self-acceptance helps rebuild confidence and self-worth.
Ways to Practice Self-Acceptance:
Affirming identity through positive self-talk → Replacing self-criticism with self-love.
Engaging in LGBTQ+ advocacy → Fighting homophobia boosts confidence.
Surround yourself with accepting individuals → Avoiding toxic environments.
Creating a “self-love” routine → Regular self-care, affirmations, and LGBTQ+ cultural engagement.
The Mental Health Benefits of Self-Acceptance:
Higher self-esteem → More confidence in one’s identity.
Lower anxiety levels → Reduces stress related to coming out or societal pressures.
Less risk of depression and suicidal ideation → Encourages self-love and hope for the future.
Self-acceptance therapy, positive affirmations, and LGBTQ+ support systems help overcome internalized homophobia, depression and self-esteem issues.
Thriving Despite Homophobia
Emotional resilience, therapy, social support, and self-acceptance are key strategies to protect LGBTQ+ mental health from homophobia.
LGBTQ+-affirming therapy is crucial in healing past trauma and reducing mental distress.
Community support and positive self-affirmations foster confidence and self-love.
By adopting these coping mechanisms, LGBTQ+ individuals can empower themselves, build emotional resilience, and live authentically despite societal challenges.
Advocacy & Fighting Against Homophobia: Creating a Safer and Inclusive Society
Homophobia’s mental health impact extends far beyond individual experiences—it is a societal issue that requires collective action. Advocacy, policy changes, education, and inclusive workplace initiatives can help create a world where LGBTQ+ individuals feel safe, valued, and supported.
Why is Advocacy Important?
Lowers homophobia-related depression, PTSD, and suicidal ideation.
Promotes LGBTQ+ rights and legal protections in workplaces and schools.
Encourages mental health awareness and access to supportive resources.
This section explores the role of advocacy, policy improvements, and workplace/school inclusivity in reducing homophobia’s negative effects on mental health.
The Role of Advocacy in Reducing Homophobia
Why Does LGBTQ+ Advocacy Matter?
Advocacy promotes equal rights, legal protections, and mental health awareness. Countries with LGBTQ+ protections report lower levels of depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation among LGBTQ+ individuals.
How Advocacy Helps LGBTQ+ Mental Health:
|
Advocacy Action |
Mental Health Benefit |
|
LGBTQ+ Education in Schools |
Reduces bullying & improves mental health |
|
Workplace Anti-Discrimination Laws |
Lowers stress & job-related anxiety |
|
Accessible Mental Health Resources |
Provides support for homophobia PTSD & trauma |
Additional Advocacy Efforts That Improve LGBTQ+ Mental Health:
Fighting for LGBTQ+ rights in health care → Ensures equal medical and mental health access.
Challenging discriminatory laws → Protects LGBTQ+ individuals from legal oppression.
Encouraging media representation → Increases positive portrayals of LGBTQ+ identities.
Graph:
Pyramid Chart → Showcasing different levels of advocacy, from basic rights activism to full social inclusion.
Government Policies & LGBTQ+ Mental Health
Countries with strong LGBTQ+ rights report lower rates of homophobia and mental health effects.
Access to mental health care is better in LGBTQ+-inclusive countries.
LGBTQ+ Rights & Mental Health Protection by Country (Table Representation)
|
Country |
LGBTQ+ Protections |
Impact on Mental Health |
|
Canada |
Strong LGBTQ+ protections |
Low levels of homophobia PTSD & depression |
|
USA |
Varies by state |
LGBTQ+ suicide rates higher in discriminatory states |
|
India |
Decriminalized homosexuality but lacks full protections |
LGBTQ+ mental health issues still prevalent |
|
Sweden |
LGBTQ+ rights fully protected |
Lowest LGBTQ+ anxiety disorder rates globally |
|
Russia |
No LGBTQ+ protections, legal discrimination |
Highest rates of LGBTQ+ PTSD & suicide |
If you're struggling with homophobia-induced anxiety or depression, searching for a psychologist near me can help you find LGBTQ+-affirming therapy to support your mental well-being.
What We Learn from Global LGBTQ+ Policies:
Strong LGBTQ+ laws directly correlate with lower mental health struggles.
Countries with restrictive laws show higher depression & suicide rates among LGBTQ+ individuals.
Access to LGBTQ+-friendly therapy is a key factor in lowering mental health distress.
The Role of Schools & Workplaces in LGBTQ+ Inclusion
LGBTQ+ inclusion in schools and workplaces is critical to ensuring mental well-being, safety, and opportunities for LGBTQ+ individuals.
How Schools & Workplaces Can Support LGBTQ+ Mental Health:
LGBTQ+ anti-bullying programs → Reduce depression, PTSD, and social anxiety.
Inclusive workplace hiring policies → Lower job-related stress and discrimination.
Mental health resources specifically for LGBTQ+ individuals → Ensure safe, affirming therapy options.
Workplace Inclusion and LGBTQ+ Mental Health:
|
Workplace Policy |
Mental Health Benefit |
|
Zero-Tolerance Discrimination Policy |
Reduces LGBTQ+ workplace anxiety |
|
Employee Resource Groups (ERGs) |
Provides support networks and community |
|
Mental Health Days for LGBTQ+ Staff |
Encourages self-care & stress reduction |
|
Diversity Training |
Lowers bias and workplace homophobia |
How LGBTQ+ Inclusion in Schools Helps Mental Health:
LGBTQ+ students in inclusive schools report 50% lower depression rates.
Schools with LGBTQ+ clubs (e.g., GSAs) reduce LGBTQ+ teen suicide attempts by 40%.
Pronoun inclusion policies help transgender students feel safer and more accepted.
How Media & Culture Shape LGBTQ+ Mental Health
The Influence of Media on LGBTQ+ Mental Health
Positive LGBTQ+ representation → Increases self-confidence and social belonging.
Harmful media portrayals → Reinforce negative stereotypes and internalized homophobia.
What Can the Media Do to Reduce Homophobia?
More LGBTQ+ characters in movies and TV → Increases representation and visibility.
Less censorship of LGBTQ+ themes → Encourages open discussions about LGBTQ+ identity.
Highlighting real LGBTQ+ stories → Reduces stigmatization and isolation.
A Collective Fight Against Homophobia
Advocacy, policy changes, school and workplace inclusivity, and media representation are crucial in reducing homophobia’s mental health effects.
Countries with LGBTQ+ protections show lower rates of anxiety, PTSD, and suicidal ideation.
Workplace and school inclusion programs improve LGBTQ+ well-being and job satisfaction.
Representation in media and culture significantly affects self-esteem and mental health outcomes.
By working together through advocacy, education, and policy reforms, we can create a world where LGBTQ+ individuals feel safe, empowered, and mentally healthy.
About the Author
Sneha Kanavaje is an esteemed psychologist at Click2Pro, renowned for her unwavering dedication to promoting mental health and emotional well-being. With years of experience in clinical psychology, Sneha specializes in addressing complex mental health challenges, particularly those stemming from discrimination, trauma, and societal stigma. Her expertise in LGBTQ+ mental health advocacy, combined with her compassionate approach, has made her a trusted voice in the field. Through her work at Click2Pro, she empowers individuals to overcome emotional barriers, build resilience, and lead fulfilling lives. Sneha's insights reflect her deep commitment to fostering an inclusive and mentally healthy world.
Conclusion: Breaking the Cycle of Homophobia & Mental Health Crisis
Why Homophobia is More Than Just a Social Issue
Homophobia is not just about prejudice and discrimination—it is a public health crisis that has severe psychological, social, and emotional consequences for LGBTQ+ individuals.
The effects of homophobia on mental health are well-documented and devastating, leading to:
Chronic anxiety, PTSD, and depression.
Substance abuse and self-destructive behaviors.
Higher rates of suicidal ideation and self-harm.
Social isolation, workplace discrimination, and family rejection.
While progress has been made in some parts of the world, millions of LGBTQ+ individuals still face daily struggles with homophobia in their homes, schools, workplaces, and healthcare systems.
The Mental Health Toll of Homophobia:
LGBTQ+ individuals are 2.5 times more likely to experience mental health disorders due to homophobia.
Homophobia self-esteem issues lead to higher rates of social withdrawal, substance abuse, and emotional distress.
Access to LGBTQ+-affirming therapy and community support significantly reduces depression and suicidal thoughts.
Scientific Studies Confirm the Mental Health Impact of Homophobia
Extensive research has shown direct correlations between homophobia and mental health decline. Here are some of the key findings:
Anxiety & Depression:
LGBTQ+ individuals in homophobic environments are 3 times more likely to develop anxiety disorders and panic attacks.
Fear of discrimination leads to chronic stress and emotional exhaustion.
PTSD & Emotional Trauma:
Hate crimes, bullying, and family rejection cause long-term PTSD symptoms in LGBTQ+ individuals.
Transgender individuals face the highest rates of PTSD due to gender-based discrimination and violence.
Substance Abuse & Risky Behaviors:
30-40% of LGBTQ+ individuals struggling with internalized homophobia turn to substance abuse as a coping mechanism.
Alcohol and drug dependency rates are significantly higher among closeted individuals due to social isolation.
Suicidal Ideation & Self-Harm:
LGBTQ+ youth are 4 times more likely to attempt suicide due to family rejection and bullying.
Transgender individuals with no family support face suicide rates as high as 50%.
Graph:
Ladder Chart → Showing the mental health decline in LGBTQ+ individuals exposed to different levels of homophobia (e.g., bullying, workplace discrimination, lack of therapy access).
Final Summary Table: How Homophobia Affects Mental Health
|
Mental Health Issue |
Cause |
Effect on LGBTQ+ Individuals |
|
Homophobia Anxiety Disorders |
Fear of discrimination |
Social withdrawal, panic attacks |
|
Internalized Homophobia Depression |
Self-hate & guilt |
Chronic sadness, low self-esteem |
|
Homophobia PTSD |
Hate crimes, bullying |
Nightmares, flashbacks, emotional numbness |
|
Homophobia Substance Abuse |
Coping with rejection |
Increased risk of addiction |
|
Homophobia Suicidal Ideation |
Social rejection, loneliness |
Higher suicide risk |
What Needs to Change?
To break the cycle of homophobia and its devastating mental health impact, the following steps must be taken:
Stronger legal protections against LGBTQ+ discrimination.
Increased access to mental health care for LGBTQ+ individuals.
LGBTQ+ education in schools to prevent bullying and discrimination.
Workplace policies that ensure a safe, inclusive environment.
Stronger Legal Protections Against LGBTQ+ Discrimination
Countries with LGBTQ+ protections report significantly lower rates of mental health issues. Governments must:
Enforce anti-discrimination laws in workplaces, schools, and healthcare settings.
Ban harmful practices like conversion therapy, which worsens internalized homophobia PTSD.
Provide legal protections for transgender individuals against hate crimes and workplace discrimination.
Impact of Legal Protections on LGBTQ+ Mental Health:
Suicide rates among LGBTQ+ youth drop by 50% in countries with strong anti-discrimination laws.
Job-related stress and anxiety decrease when workplace protections are in place.
Increased Access to LGBTQ+-Affirming Therapy & Mental Health Care
LGBTQ+-friendly therapy significantly reduces depression and suicidal ideation.
Online mental health platforms allow LGBTQ+ individuals to seek help in safe spaces.
Support groups and peer counselling provide emotional validation and coping mechanisms.
What Needs to Change?
More LGBTQ+-inclusive mental health providers.
Insurance policies that cover LGBTQ+ therapy and hormone treatments.
Government's funding mental health initiatives specifically for LGBTQ+ individuals.
Building a Future Free from Homophobia
Breaking the cycle of homophobia starts with systemic changes in:
Education: Schools must teach LGBTQ+ inclusion to prevent bullying.
Workplaces: Companies must ensure equal opportunities for LGBTQ+ employees.
Healthcare: LGBTQ+ mental health services must be affordable and accessible.
Media Representation: Positive LGBTQ+ representation reduces stigma and encourages self-acceptance.
The Ultimate Goal: A World Where LGBTQ+ Individuals Thrive
A society where LGBTQ+ individuals don’t fear discrimination, rejection, or violence.
A mental health system that supports LGBTQ+ identities without stigma.
Stronger policies that protect LGBTQ+ people in every aspect of life.
FAQs
1. How does homophobia affect mental health?
Homophobia leads to homophobia psychological distress, causing anxiety, PTSD, depression, and substance abuse. Studies show LGBTQ+ individuals face 60% more mental health issues than heterosexual individuals.
2. Can homophobia cause PTSD?
Yes, homophobia and PTSD is real. Many LGBTQ+ individuals develop PTSD symptoms after experiencing discrimination, violence, or bullying. Survivors of conversion therapy and hate crimes are at a higher risk.
3. What are the effects of internalized homophobia?
Internalized homophobia depression causes low self-esteem, suicidal thoughts, and risky behaviors. LGBTQ+ individuals often struggle with self-acceptance due to societal stigma.
4. How can LGBTQ+ individuals cope with homophobia?
Therapy, emotional support, and LGBTQ+ community engagement are the best homophobia coping mechanisms. Support from friends and mental health professionals helps combat homophobia anxiety disorders and self-esteem issues.
5. What are the long-term effects of homophobia?
Chronic stress, substance abuse, suicidal ideation, and workplace discrimination are long-term impacts of homophobia. LGBTQ+ individuals often struggle with mental health disorders due to ongoing stigma and exclusion.
6. How can society help LGBTQ+ individuals facing homophobia?
Society can reduce homophobia mental health effects by enforcing anti-discrimination laws, providing mental health resources, and promoting LGBTQ+ education.
7. What should I do if I’m struggling with mental health due to homophobia?
Seek LGBTQ+-affirming therapy, connect with support groups, practice self-care, and engage in advocacy. Resources like The Trevor Project, LGBTQ+ helplines, and therapy platforms provide immediate support.
Final Call to Action: Be the Change
Homophobia is a systemic issue that needs urgent intervention. Whether you are a member of the LGBTQ+ community or an ally, you can help break the cycle of discrimination and support mental health advocacy.
What You Can Do:
Support LGBTQ+ organizations.
Speak up against discrimination.
Educate yourself and others about LGBTQ+ mental health.
Create safe spaces for LGBTQ+ individuals in your workplace and community.
Transform Your Life with Expert Guidance from Click2Pro
At Click2Pro, we provide expert guidance to empower your long-term personal growth and resilience. Our certified psychologists and therapists address anxiety, depression, and relationship issues with personalized care. Trust Click2Pro for compassionate support and proven strategies to build a fulfilling and balanced life. Embrace better mental health and well-being with India's top psychologists. Start your journey to a healthier, happier you with Click2Pro's trusted online counselling and therapy services.






